Fun with Spatial Dimensions in Apache Druid
Today, I am going to look at geospatial data in Apache Druid in some more detail. Back in September, we learned how to ingest these data into Druid.
It turns out that a spatial dimension is in fact not much more than a string, in which x and y coordinate (or latitude and longitude) are separated by a comma. (You could also have more than two dimensions, but the filtering semantics are tailored for two dimensions.)
Data Generation
First, we need to generate some test data. I am using the Python Faker module in a small script like this:
import json
from faker import Faker
fake = Faker()
def main():
print("latitude,longitude,place_name,country_code,timezone")
for i in range(0, 10000):
place = fake.location_on_land()
print(','.join(place))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Ingest these data into Druid as described in my previous post.
Querying
Let’s start with a simple SQL query. I want a list of places with their coordinates, and how often they occurred in my file:
SELECT
coordinates,
place_name,
COUNT(*)
FROM
geo_data_ww
GROUP BY 1, 2
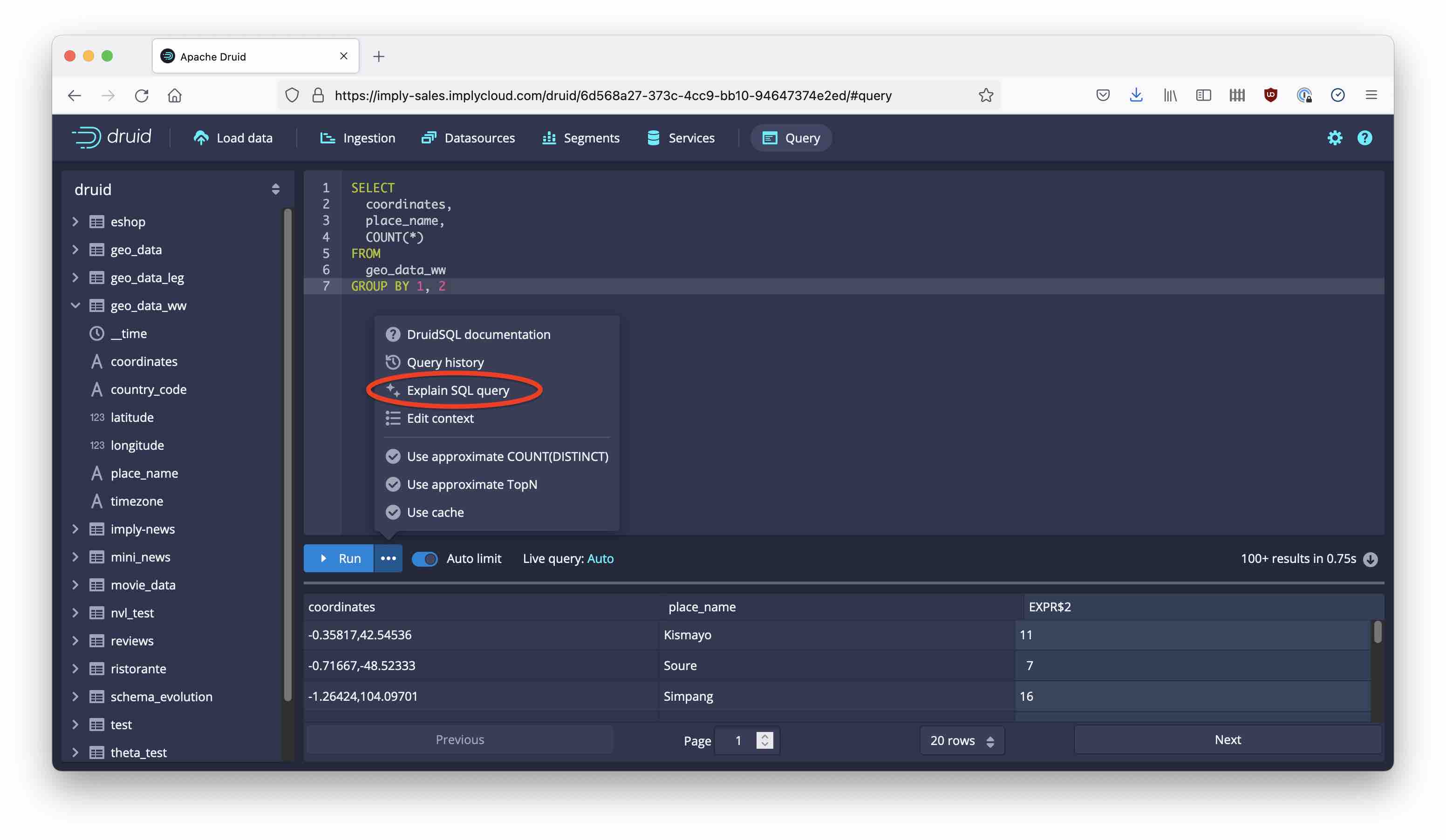
In order to do my spatial magic, I need to convert this SQL code to a Druid native query. This is an easy interactive process in the Druid query console.
First, use the Explain function to show the Druid native query that is generated:
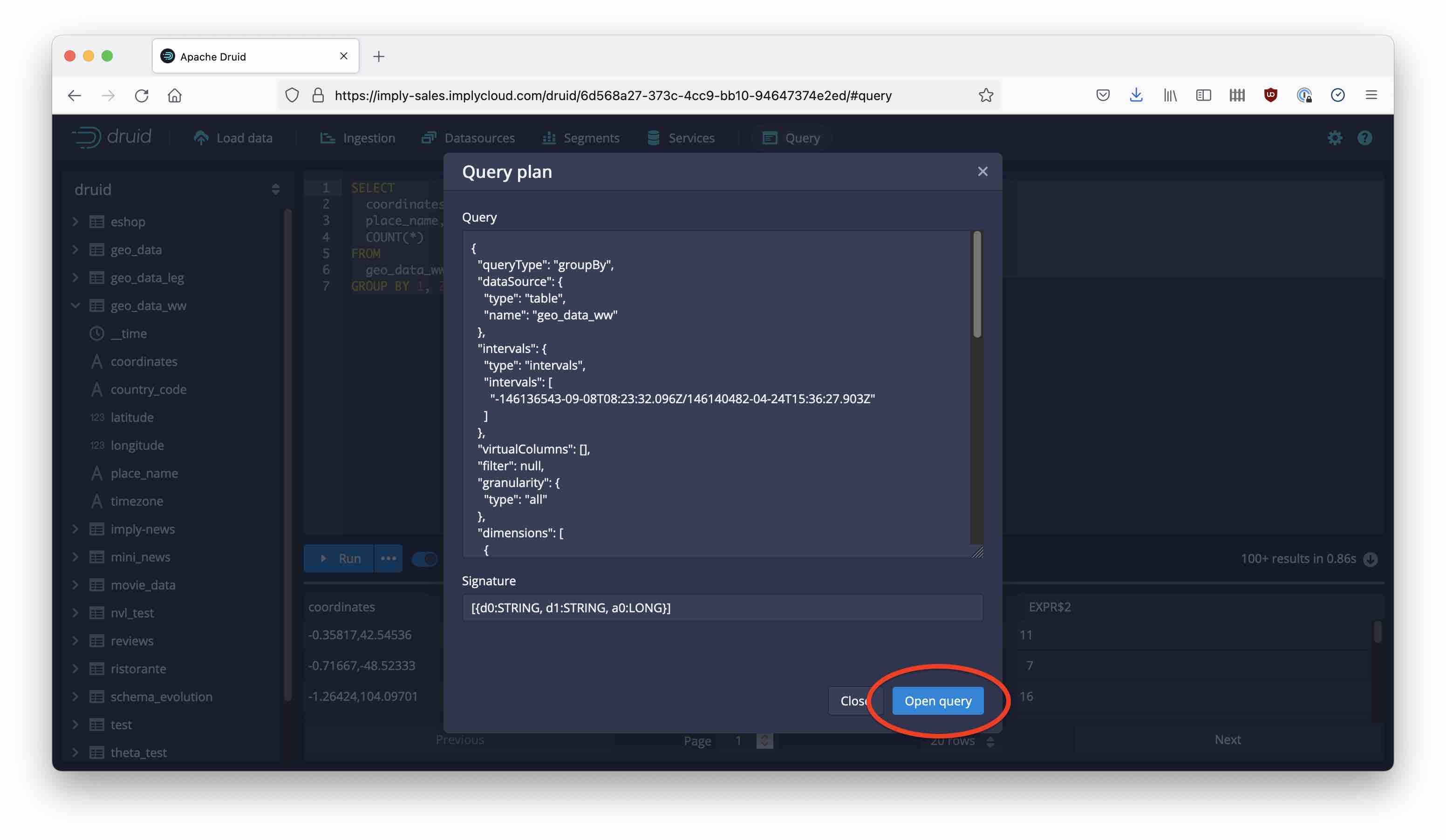
Then, use the Open Query button to open the native query in the editor, instead of the SQL.
Spatial Filtering!
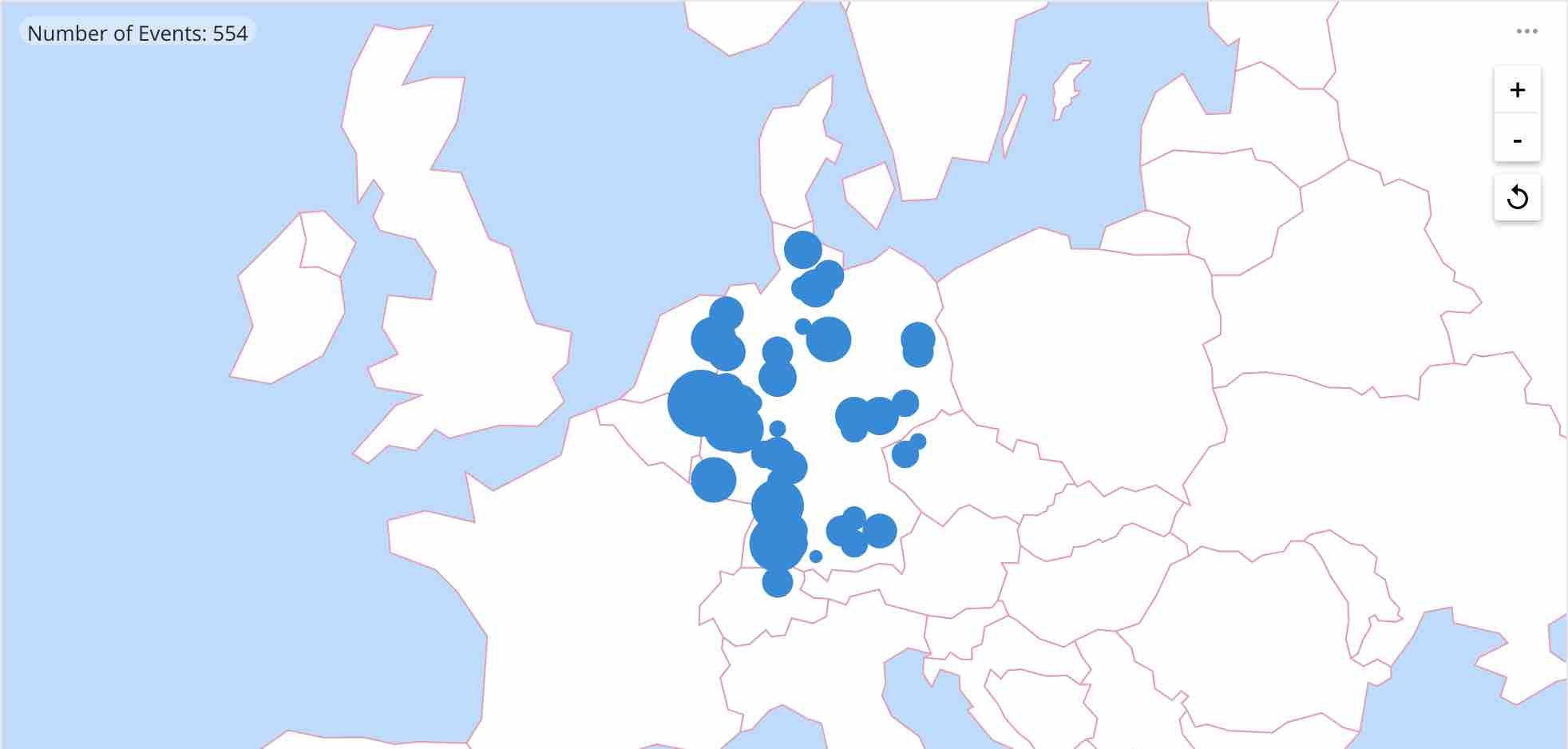
Now, let’s introduce a filter! I am going to try and select only the places within a rectangle that roughly contains my home country, Germany. So I want to cover an area from 47°N to 55°N latitude, and from 6°E to 15°E longitude.
Find the place in the query where it says "filter": null, and replace it by the following snippet:
"filter": {
"type": "spatial",
"dimension": "coordinates",
"bound": {
"type": "rectangular",
"minCoords": [47.0, 6.0],
"maxCoords": [55.0, 15.0]
}
}
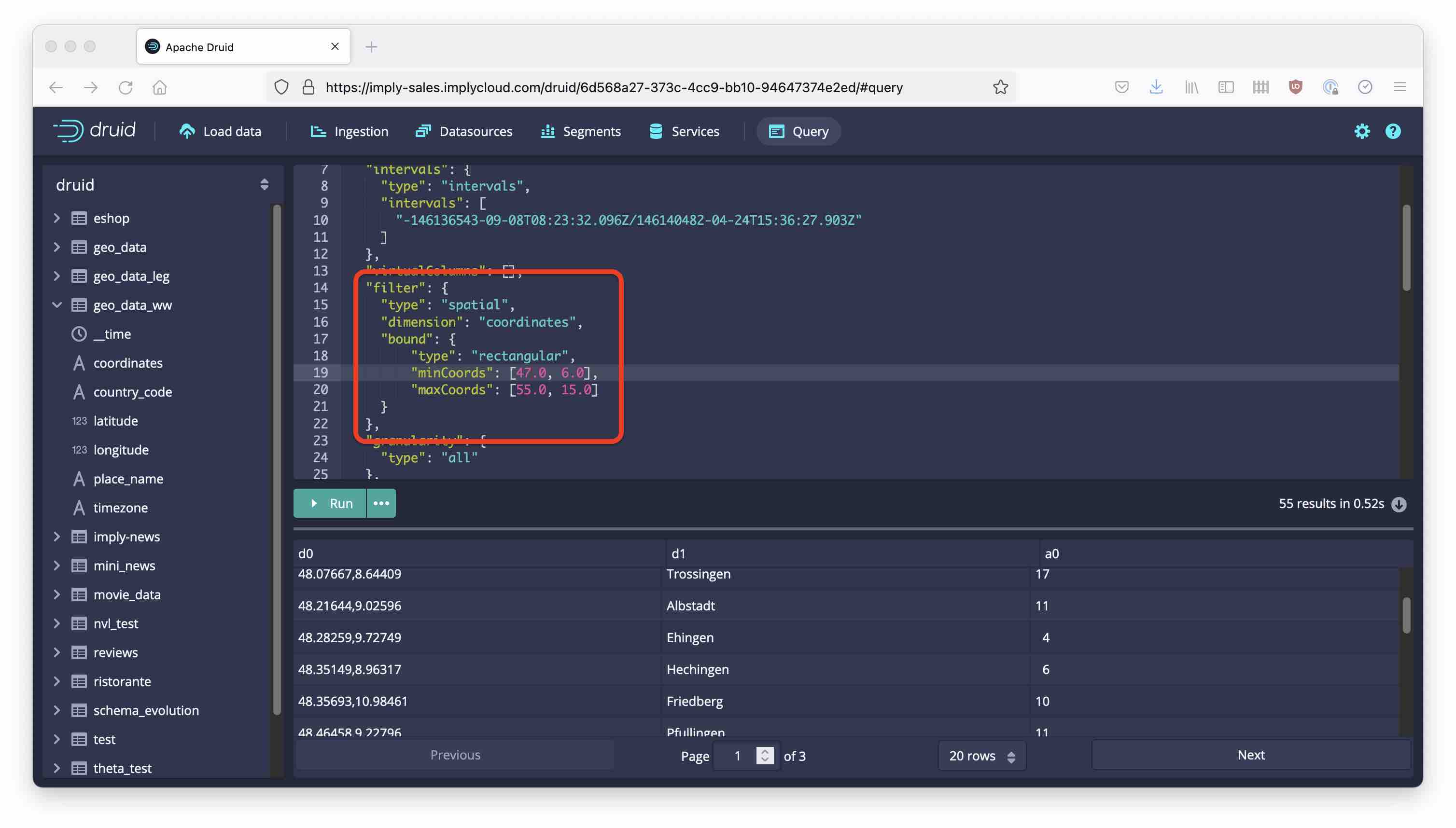
Note how the places that are listed in the result are almost all in Germany! You can also define circle and polygon filters. Spatial dimensions and filters are documented here.
Learnings
- Spatial dimensions are encoded as strings.
- Spatial filters are supported by the Druid native query language only.
- You can use the
Explainfunction in the Druid console to convert a SQL query into its Druid native equivalent.